스포트라이트
Music Coordinator, Music Consultant, Music Licensing Supervisor, Music Clearance Supervisor, Music Placement Supervisor, Music Synchronization Supervisor, Music Rights Supervisor, Music Selection Supervisor, Music Editor, Music Catalog Manager
Imagine watching a movie or TV show that didn’t have any music. It just wouldn’t be the same. Music is an integral part of the entertainment media we watch, and each production has a music department behind it all. In charge of that team is a Music Supervisor!
Music Supervisors help find spots where music will help augment what’s happening on the screen. They find creative, pre-existing musical options to present to the director or writers. Many also work on commercials and video games. Once music choices are made, their team works with the license holder (such as a recording studio) to obtain permission to use the music. Some songs can cost up to hundreds of thousands of dollars to use, such as rock band AC/DC’s “Thunderstruck” which shows how important the right soundtrack is when it comes to boosting production value!
- Having creative involvement with films, TV shows, ads, and video games
- Helping to boost the entertainment value of productions
- Contributing to the commercial success of productions, which can lead to more job creation
근무 일정
- Music Supervisors may work full- or part-time jobs, depending on their position. Some work in a freelance contract capacity while others are employed by media companies where they get to work on multiple projects. Most work in or around entertainment hub cities like Los Angeles and New York City.
일반적인 의무
- Attend pre-production meetings with directors, writers, and producers to hear about the ideas for the production (i.e, the show, ad, game, or film) and discuss suitable music styles and attributes that match the production’s aesthetic
- Discuss and agree upon budgets for licensing existing music or hiring artists to write and perform new music
- Watch rough versions of the production to identify where music should be inserted
- Create lists of suggested songs or musical pieces that fit particular scenes/sequences and can synchronize without much editing
- Review list suggestions with directors and writers, or, if given the authority, make the song selections
- Collaborate with composers as needed for adding original scores versus pre-existing music
- Reach out to music license holders (such as record studios) to discuss buying the rights to use a song. Negotiate fees and terms of use
- Find suitable artists to write and perform original songs and scores, or to do covers of existing songs (once rights are obtained)
- In some cases, work with performers who will star in the production itself
- Meet with label representatives or artists as needed to discuss the mutual benefits of their involvement with a production, including exposure and royalties
- Many pre-existing songs become virtually synonymous with the films or shows they are featured in
- Use cue sheets to track all songs used in the final production
- Ensure artists are credited appropriately in all film and promotional credits, and make sure royalties are sent out
- Work closely with the music team, production and post team, and other involved crew (such as choreography, if a scene must be closely synched to a piece of music)
- Keep track of the production and post-production schedules so that all work is completed on time, with applicable rights firmly secured
- Work with promotional teams to assess music to be used for commercials, social media ads, etc.
추가 책임
- 최신 음악, 아티스트, 트렌드에 대한 최신 정보 확인
- Study a broad range of music genres
- Build strong relationships with artists, record labels, and other musical intellectual property holders
- Train and mentor music team crew members
소프트 스킬
- 세부 사항에주의
- 창조적인
- 목표 지향적
- 이니셔티브
- 리더십 기술
- 관찰력
- 조직
- 환자
- 설득력 있는
- 문제 해결
- 강력한 의사 소통 기술
- 강력한 연구 기술
- 팀워크
- 시간 관리
기술 능력
- 문화적 인식
- Familiarity with music licensing, rights, and royalties
- 음악에 대한 좋은 '귀'
- Knowledge of cue sheets
- Solid grasp of video production
- Understanding of copyright infringement laws
- Very broad knowledge of many music genres, artists, and history
- Advertising companies
- Film, television, and video game studios
- Production companies
- 자영업자
- Small music-supervision companies
Music Supervisors have plenty of responsibility riding on their shoulders because songs and scores can make or break a production. The right music can dramatically enhance scenes and make them more memorable, while mismatched music can distract audiences or destroy an otherwise great scene.
There is a ton of artistic license involved and many choices may not resonate with every director, writer, or viewer. Sometimes bold musical choices might seem incongruous with a film’s subject matter, yet end up working out perfectly—such as with Pulp Fiction’s eclectic 16-song soundtrack, the 70s jams from Guardians of the Galaxy’s “Awesome Mix Vol. 1,” or George Lucas’ wise decision to use John Williams’ original, orchestral score for Star Wars!
Long story short, it’s easy to play it “safe,” but to really stand out and make a name for yourself, you’ll have to take chances from time to time!
Movies have always relied on music to augment them, but now TV series and video games have big budgets, too, and can afford to license existing songs from top artists!
Streaming services have had a huge impact in this arena, with companies like Disney, Netflix, Apple, and Amazon investing big bucks to put out content that’ll draw subscribers. Part of that strategy involves producing incredible original scores as well as licensing hits from popular artists (such as Stranger Things and its litany of catchy 80s tunes).
Meanwhile, games like Grand Theft Auto have gone truly over the top when it comes to music partnerships, with its in-game radio stations playing hundreds of licensed songs across several genres.
Music Supervisors are like walking encyclopedias of music, and such breadth and depth of knowledge typically come from growing up as an avid music lover. Many are musicians themselves and may have started playing an instrument in their youth.
In addition to knowing a great deal about music, they’re often long-time movie buffs who can tell when a bit of song or score can beef up a scene. And because they work with artists and record labels, Music Supervisors need incredible people skills…which they likely picked up from engaging in school or extracurricular activities!
- There is no specific educational route to becoming a Music Supervisor, but Zippia notes that ~72% of workers in this field hold a bachelor’s degree
- The most common majors are music, entertainment business, and photography
- Music courses may include music theory (melodies, rhythms, tempos), composition, and arrangement
- Music Supervisors also need to study or learn about:
- The basics of how films, TV shows, commercials, and/or video games are made
- Details about intellectual property, licensing rights, royalties, and marketing
- How to negotiate with artists and record labels
- An internship with a Music Supervisor is a great way to gain practical real-world experience, regardless of whether you complete a college degree or not
- Anyone can take ad hoc Music Supervisor courses online, such as those listed by Gemtracks. Examples include:
- UCLA Extension’s Music Supervision Course
- Udemy’s Music Business: Find Music Publishing and Licensing Placement
- Skillshare’s Creating Music Licensing Gold
- Some schools offer certificates such as Berklee’s online Music Supervision Professional Certificate
- If you decide to pursue a bachelor’s or master’s to help you land a job as a Music Supervisor, look for music or music business programs that feature courses related to the career field.
- 항상 수업료와 기타 비용을 비교하고 장학금 및 재정 지원 옵션을 검토하세요.
- Check out the program’s alumni to see how many made it into the music and entertainment business!
- Read about the career field and how people get started. Check out Tidal’s So You Want to be a Music Supervisor?
- 다양한 음악을 감상하세요. 스트리밍 음악 서비스에 계정을 등록하고 다양한 방송국을 시청하여 새로운 아티스트와 노래를 접할 수 있습니다.
- Watch some of your favorite movies and shows and take note of where music is added and how it compliments the scene it is accompanying
- Read about how music is selected for commercials and video games
- Train your aural skills so you can develop an “ear” for music
- Take music classes in high school to learn about theory, composition, and arrangement
- Consider learning an instrument, either in band, via private lessons, or on your own!
- Boost your odds of getting hired by finishing a relevant bachelor’s degree, or at least a certificate program
- Volunteer or apply to part-time jobs or freelance gigs where you can practice your skills, such as on small-budget independent film projects or even YouTube videos
- Note, there are many sites where you can access royalty-free music to include in videos
- Try your hand at freelancing on sites like Upwork, Fiverr, or Mandy
- Apply to internships with music labels and start working on building your professional network
- Watch YouTube videos featuring interviews with Music Supervisors and tips about the profession
- Become familiar with the sites musicians use to connect their work with entertainment industry projects. After all, while Music Supervisors look for talent, talent is out there looking for them, too! (See our list of Resources > Websites)
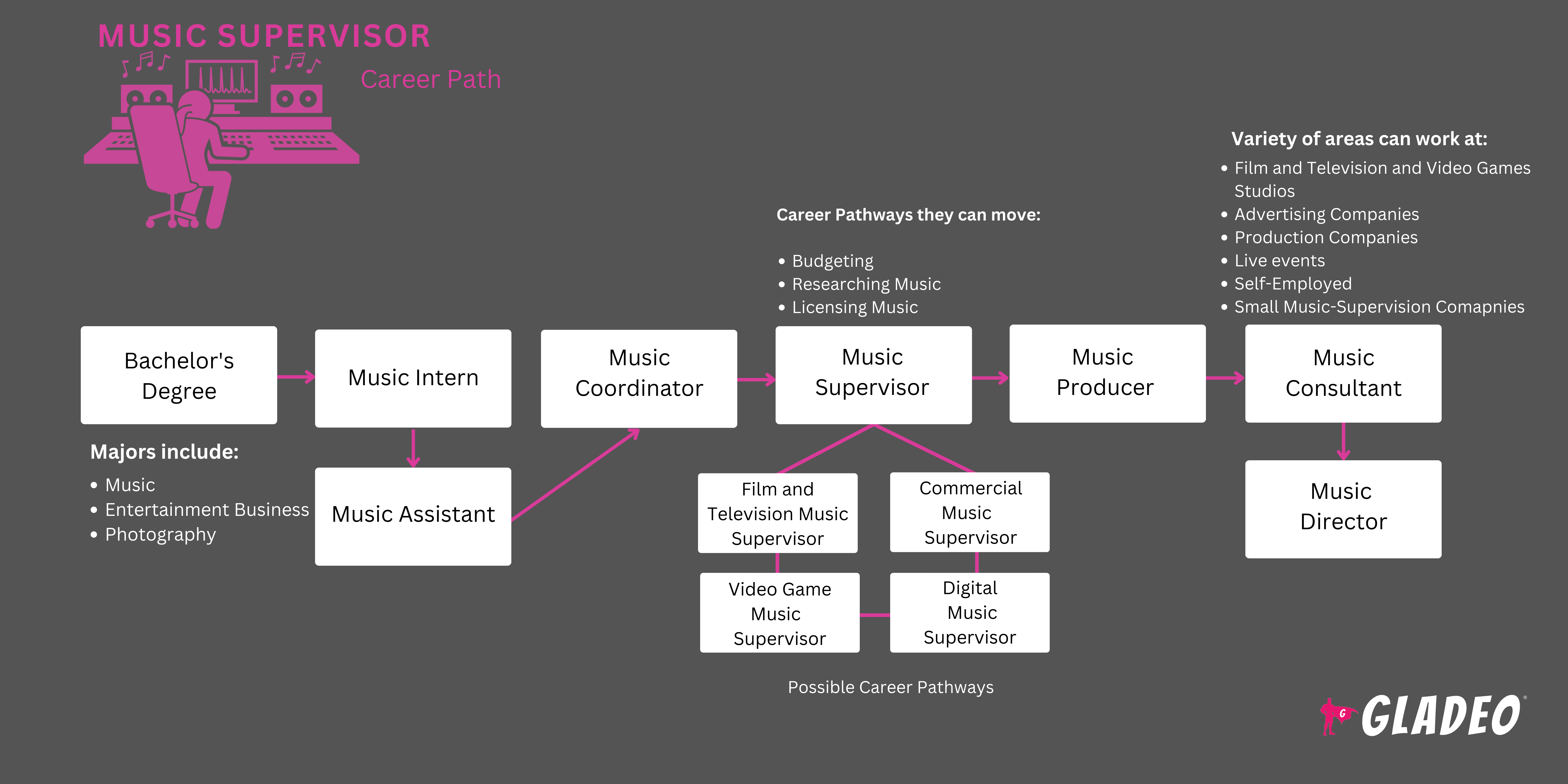
- There isn't a straightforward path to becoming a Music Supervisor. As with other career fields, supervisors need to gain considerable experience first!
- Many Music Supervisors are self-employed or work on a project basis. They need a website and existing connections in the industry to get started
- Some find work through freelance sites, but it can be difficult to achieve a sustainable income model that way
- The website should include a portfolio of your applicable work (see Kelsey Mitchell’s for an example). If you haven’t worked on any professional productions, you can still create samples of your own using royalty-free music
- Showcase your work on Instagram, TikTok, and other social media platforms (as long as it doesn’t breach copyright policies)
- Those who want to apply to full-time positions need sufficient experience. This is gained over time but can start with a mixture of suitable volunteer work, part-time jobs, internships, and related entry-level positions that lead to working with a project’s music team
- Suitable entry-level might include working with a talent agency or record label or serving as an assistant to a film producer or director
- Eventually, you’ve got to work your way into the music department, ideally helping the Music Supervisor so you can learn the ropes!
- Having a relevant degree or certificate can help boost your odds of getting interviewed
- Carefully review job postings on Indeed, ZipRecruiter, and industry job boards. Upload your resume on these sites, when possible, so recruiters can find you even when you’re not actively looking
- Create an outstanding profile on LinkedIn and advertise yourself as Open for Business
- 대학 수업을 수강하는 경우, 프로그램 교수진에게 도움이 될 만한 팁이나 인맥이 있는지 물어보세요.
- 개인 추천을 해주거나 작업에 대한 리뷰를 작성해 줄 수 있는 고객이나 교사에게 연락하세요.
- Attend film events and try to hobnob with industry insiders
- Music Supervisors are already pretty high up in the production team
- Those who work for an employer may qualify for a raise by consistently delivering high-quality work that enhances the production value and stays within budget and timeframes
- Full-time employees who aren’t reaching their goals can also launch their own companies and be their own boss
- In contrast, those who are self-employed in a freelance/contract capacity might want to apply for a full-time job that offers regular pay and job security!
- Doing great work helps land larger projects, but it can take time to gain a solid reputation in the entertainment business. It’s vital to constantly work on growing your network and influence
- Consider relocating to an area where there is a higher demand for Music Supervisors, like LA or NYC
- Participate in professional organizations such as Guild of Music Supervisors
- Collaborate well with artists, music producers, record labels, and talent agencies. Always negotiate in good faith and help artists gain exposure for their work while being compensated fairly and in accordance with agreed-upon terms
웹사이트
- Beta Patrol
- Boost Collective
- Brewman Music
- Chloe Raynes
- Chop Shop Music
- Concord
- Copyright MV
- Creative Control
- Cutting Edge Group
- Evolution Music Partners
- Format Entertainment
- Greenspan Kohan
- GSA Music
- Guild of Music Supervisors
- Harvest Creative Services
- HD Music Now
- Hear It Clear It
- Hit The Ground Running
- Inaudible Productions
- Michael Welsh
- Music Supervisors
- Neophonic
- Nimrod Sound
- No Mission Music Supervision
- North Music Agency
- Radar Music Group
- Ralph Sall
- Reelent
- Rights Workshop
- Search Party
- Songfinder
- Songrunner Entertainment
- Songwriter Universe
- Stef Angel Music
- Syncalicious
- Tetragram
- TLS Music Services
- Woodwyn Lane
책
- Hey! That’s My Song!: A Guide to Getting Music Placements in Film, TV, and Media, by Tracey Marino
- Shortcuts to Songwriting for Film & TV: 114 Tips for Writing, Recording, & Pitching in Today's Hottest Market, by Robin Frederick
- Thinking In Sync: A Primer on the Mind of a Music Supervisor, by Amanda Krieg Thomas
Working as a Music Supervisor can be a rewarding experience, but there are many other career fields within the entertainment and media industries. If you’re curious about some alternatives, consider the following options!
- A&R 담당자
- Actor
- Audio/Sound Engineer
- 안무가
- 시네마토그래퍼
- 감독
- Music Director and Composer
- 음악가
- 사진사
- Producer
- 생산 디자이너
- 사운드 디자이너
- Video Editor
뉴스 피드
주요 채용 정보

온라인 과정 및 도구








